In the field of HR, you’ve likely heard the acronyms HRIS, HRMS, and HCM, which are often used interchangeably. Each acronym refers to a software solution designed to streamline HR processes and empower HR leaders with more advanced technology. The systems are:
HRIS: Human resources information system
HRMS: Human resources management system
HCM: Human capital management
Read on for the differences, similarities, and benefits of the three systems.
The Difference Between HCM vs HRIS vs HRMS
While these terms are often used interchangeably, each system has unique characteristics and capabilities. Let’s start with a brief definition of each:
- HRIS: A form of HR software used to help businesses organize and manage people-related data, such as employee demographic information, employee job information, and benefits selections.
- HRMS: An integrated suite of HR applications that combines data with core HR functions like payroll, benefits administration, and employee self-service capabilities.
- HCM: A comprehensive strategic platform that views employees as valuable assets and streamlines HR functions, like talent acquisition, development, performance management, and workforce analytics, into strategic advantages.
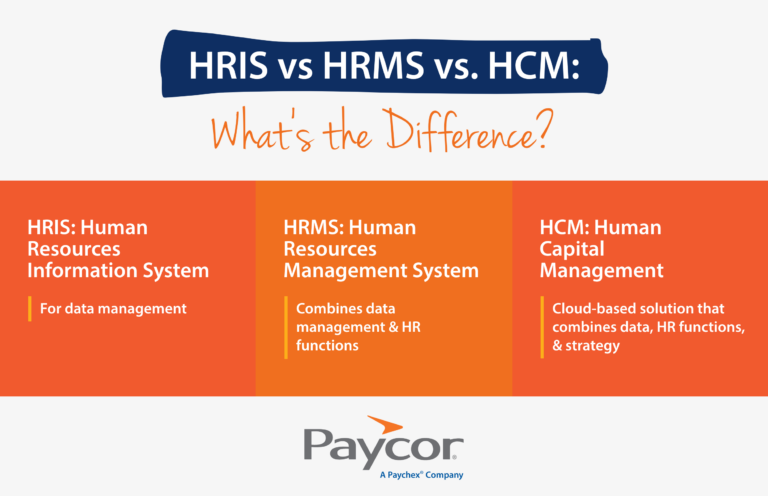
To put it simply:
An HRIS is for data management.
An HRMS combines data management and HR functions.
An HCM is a cloud-based solution that combines data, HR functions, and strategy.
Taking a Closer Look: HRIS, HCM, and HRMS
Take a deeper dive into exactly what each system does and their unique benefits.
What’s an HRIS?
An HRIS serves as the digital backbone of HR operations, functioning primarily as a centralized database for employee information. This system digitizes and automates basic HR processes, replacing traditional paper-based record-keeping with efficient electronic data management.
An HRIS typically handles core administrative functions such as employee demographics, job history, organizational charts, and basic reporting. It serves as a single source of truth for employee data, ensuring accuracy and accessibility across the organization.
Benefits of HRIS
- Enhanced data accuracy: Centralized storage eliminates duplicate records and inconsistencies that plague manual systems.
- Improved compliance:Automated record-keeping and reporting capabilities ensure adherence to labor laws and regulations.
- Increased efficiency: Reduces time spent on data entry and retrieval, allowing HR professionals to focus on strategic initiatives.
- Cost savings: Delivers savings through reduced paperwork, improved process efficiency, and better data-driven decision-making.
- Employee self-service: Empowers staff to update their own information and access important documents, reducing administrative overhead.
What’s an HRMS?
The HRMS combines the data center of an HRIS with core HR functionality. By enabling organizations to execute HR tasks through a single platform, an HRMS streamlines workflows and increases productivity.
Consolidating multiple processes into one system allows organizations to eliminate data silos and create more cohesive HR operations. The HRMS is the next level up from an HRIS.
Benefits of an HRMS
- Improved payroll accuracy: Automated data synchronization between HR records and payroll systems reduces errors and ensures timely compensation.
- Streamlined benefits administration: Integrated enrollment processes and automated compliance tracking make benefits management more efficient.
- Better management tools: Managers gain access to powerful tools for team management, including approval workflows and reporting capabilities.
- Cost effectiveness: Single system results in reduced system licensing fees, simplified training requirements, and decreased IT maintenance overhead.
- Unified analytics: Single platform supports better data analytics and reporting across all HR functions.
What is an HCM?
An HCM platform includes the data of an HRIS, the HR functionality of the HRMS, but adds another element — integrated talent management features. That’s because HCM represents a strategic approach to workforce management that views employees as valuable assets requiring investment and development.
HCM systems encompass the entire employee lifecycle, from recruitment and onboarding through performance management, learning and development, succession planning, and eventual offboarding. This comprehensive approach aligns workforce capabilities with business objectives, driving organizational success through people-centric strategies.
Benefits of an HCM
- Strategic workforce planning: Advanced analytics and predictive insights help organizations anticipate talent needs and identify potential gaps.
- Enhanced performance management: Continuous feedback and goal alignment features foster a culture of growth and achievement.
- Improved talent acquisition: Sophisticated recruiting tools streamline the hiring process and ensure better candidate matches.
- Continuous learning and development: Integrated modules support ongoing skill building and career advancement.
- Better retention: Strategic focus on human capital development leads to improved employee retention and higher productivity.
Comparing HCM vs HRIS vs HRMS Side-by-Side
Now let’s compare the platforms side-by-side.
Difference Between HCM vs HRIS
The fundamental difference between HCM and HRIS lies in their strategic approach and scope of functionality. HRIS systems focus primarily on data management and administrative efficiency, serving as sophisticated databases that digitize traditional HR record-keeping processes.
HCM platforms, conversely, emphasize strategic workforce management and talent development. While an HRIS manages information, HCM systems transform how organizations develop and utilize human capital. HCM software includes advanced features like performance management, learning management, succession planning, and workforce analytics that extend far beyond basic data storage.
The implementation timeline and complexity also differ significantly. HRIS systems typically offer faster deployment with immediate operational benefits, while HCM platforms require more extensive planning and change management to realize their strategic potential.
Difference Between HRIS vs HRMS
HRIS and HRMS systems share significant overlap in core functionality, but HRMS platforms offer broader integration and operational scope. Both systems excel at employee data management and basic HR processes, but an HRMS extends into comprehensive workforce management through integrated payroll, benefits, and self-service capabilities.
The architectural approach distinguishes these systems significantly. HRIS platforms typically focus on perfecting core HR data management functions, while HRMS systems prioritize integration across multiple HR disciplines within a unified platform.
Implementation complexity tends to be higher for HRMS systems due to their broader scope, requiring more extensive training and change management. However, this complexity often results in greater operational efficiency once fully deployed.
Difference Between HCM vs HRMS
HCM and HRMS systems represent different philosophical approaches to workforce management, with HCM software emphasizing strategic talent development and HRMS tools focusing on operational efficiency.
The strategic orientation of HCM platforms centers on maximizing human potential through sophisticated talent management processes. HRMS systems prioritize operational excellence through seamless integration of administrative functions, payroll, and benefits management.
HRMS systems excel in operational features like payroll processing, benefits administration, and compliance management. In addition to operational features, HCM platforms typically offer more advanced capabilities in performance management, learning and development, and workforce analytics.
HRIS vs HCM vs HRMS Comparison Chart
The following comparison chart offers a quick glimpse at the primary purpose, cores strengths, and use cases for an HRIS vs HRMS vs HCM.
| Feature Category | HRIS | HRMS | HCM |
| Primary Focus | Employee data management and basic HR processes | Integrated HR operations with employee data | Strategic talent management and human capital development |
| Core Strengths | Data accuracy, compliance, administrative efficiency | Process integration, payroll accuracy, operational efficiency | Talent development, performance management, workforce analytics |
| Implementation Complexity | Low to moderate | Moderate to high | High |
| Use Case | Organizations needing efficient data management | Businesses requiring integrated HR and payroll operations | Companies focused on talent development and strategic HR |
| Analytics Capabilities | Basic reporting and compliance metrics | Operational reporting and payroll analytics | Advanced workforce analytics and predictive insights |
Similarities Between HRIS vs HRMS vs HCM
Despite their distinct characteristics and primary focus areas, HRIS, HRMS, and HCM systems share fundamental similarities that reflect common goals in modern HR technology implementation. Key shared features include:
- Data centralization and accuracy: All three systems eliminate data silos and create single sources of truth for organizational information, recognizing that reliable employee data forms the foundation of effective HR operations.
- Process automation: Each platform reduces manual administrative tasks and delivers time savings and error reduction, allowing HR professionals to focus on higher-value activities.
- Compliance support: Built-in capabilities help organizations meet regulatory requirements and maintain accurate records across all system types.
- Employee self-service: All platforms empower staff to manage their own information and access important documents, reducing administrative burden on HR teams.
- Reporting and analytics: Each system type provides insights into workforce data to support data-driven decision-making at different organizational levels.
- Integration capabilities: All three recognize the need to connect with other business applications and data sources in modern business environments.
The Best HR and HCM Technology for Your Business
Gartner shows technology continues to be the highest-growing part of the HR budget. Still, selecting the optimal HR technology solution requires careful consideration of organizational needs, strategic priorities, and implementation readiness.
Key factors to consider when selecting HR technology include:
- Current HR maturity level: Assess whether your organization needs foundational improvements or strategic advancement.
- Budget and resources: Consider both initial investment and long-term operational costs.
- Integration requirements: Evaluate how new systems will connect with existing business applications.
- Scalability needs: Ensure selected solutions can grow with your organization.
- Strategic priorities: Align technology selection with broader business objectives.
How Paycor Helps
The right software provides a single source of truth for employee data and empowers HR leaders to focus on strategy. The Paycor HCM modernizes every aspect of people management from HR and payroll to benefits administration and talent development.
Customers that switched software providers to Paycor streamlined their businesses by reducing the number of HR tools and people management systems they were using by 184%.
Learn why 30,000+ customers choose Paycor for their HR software of record. Request a guided product tour.