When responding to the importance of benefits categories for the Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM)’s 2024 Employee Benefits Survey, human resource professionals overwhelmingly ranked health-related benefits at the top. And for employers with 50+ full-time employees, providing health insurance is mandatory.
“Employee benefits are crucial in attracting and retaining top talent, especially in today’s rapidly evolving workplace,” says Alex Alonso, SHRM chief data and insights officer.
With the value of the benefit, choosing the right health insurance plan for your employees proves critical. The type of health plan you offer not only impacts your employees’ access to healthcare but also affects their satisfaction, productivity, and overall well-being.
Factors to consider include affordability, accessibility, and network quality. Three popular health insurance coverage plan types are health maintenance organizations (HMO), exclusive provider organizations (EPO), and preferred provider organizations (PPO).
Read on to learn the differences of each plan type to decide which is the best fit for your overall benefits strategy.
Types of Health Plans
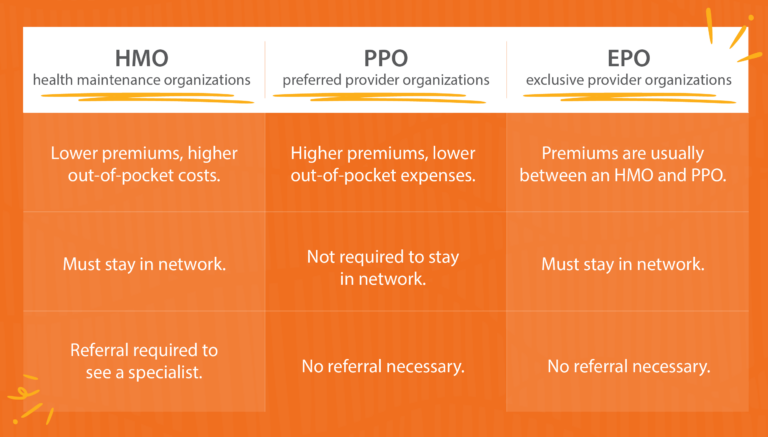
First, let’s define each:
What is an HMO?
An Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) is a health insurance plan that limits coverage to providers and hospitals within its contracted network. A covered employee typically needs to receive referrals from a primary care physician in network.
Pros of HMO:
- Lower monthly premiums and out-of-pocket costs
- Strong focus on preventive care and coordinated treatment
- Simplified claims process when care is managed through a PCP
Cons of HMO:
- Out-of-network care is usually not covered except in emergencies.
- Referrals are required for most specialist visits.
- Provider networks may be smaller and reduce choices and options.
What is a PPO?
The most common plan type offered, Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) is a health plan that contracts with providers to build a network. Covered employees pay less for seeing doctors within the preferred network.
Pros of PPO:
- There can be more flexibility for out-of-network doctors.
- Referrals are not always needed to see specialists.
- Provider networks tend to be larger.
Cons of PPO:
- Premiums and deductibles are usually higher.
- There is complex cost-sharing, especially when using out-of-network providers.
- Out-of-pocket costs can add up quickly.
What is an EPO?
An Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO) plan blends features of HMOs and PPOs. Exclusive is the key word when it comes to an EPO, which is a care plan that covers costs only if the participant goes to doctors, specialists, or hospitals in the plan’s network.
Pros of EPO:
- Lower premiums are offered.
- Referrals are not usually required for specialist visits.
- Care is streamlined within a defined provider network.
Cons of EPO:
- There is no coverage for out-of-network providers. (Emergencies may be covered.)
- Provider network may be small.
- Restrictive for employees who travel often.
Comparing Plans: HMO vs PPO vs EPO
When it comes to HMO vs EPO vs PPO, there are pros and cons to consider for all plan types. Here’s a breakdown on the main differences, including cost and network limits.
Flexibility
HMO: Limits plan participants to providers in the HMO network. Employee must choose a primary care provider (PCP) for regular checkups. For specialty care, like dermatologists or allergists, plan participants need a referral from the PCP.
PPO: Provides the most flexibility among the three plan types. Employees can see any doctor or specialist, whether they are in-network or out-of-network, without needing a referral. However, staying within the preferred network reduces costs significantly.
EPO: Combines elements of both HMO and PPO plans. Like an HMO, EPOs limit coverage to a network of providers, and employees must stay within this network to have services covered (except for emergency care). The network is typically larger than what an HMO offers. However, like a PPO, EPOs do not require referrals to see specialists.
Costs
For the employer, an HMO is typically the most economical option to implement. But it’s important to consider the cost burden healthcare places on employees, too.
HMO: Employees typically enjoy lower premiums with HMO plans. However, they may face significant out-of-pocket costs if they need to seek care outside the network, as these plans often do not cover out-of-network services. Additionally, co-pays and deductibles are usually lower.
PPO: PPO plans generally come with higher premiums compared to HMOs, making them more expensive for employers. The ability to see out-of-network providers without a referral means employees might face higher out-of-pocket costs if they choose to go outside the network, but they have the option to do so, offering a balance between cost and choice.
EPO: EPO plans typically have premiums that fall between those of HMOs and PPOs, providing a cost-effective middle ground for employers. If employees stay in network, their out-of-pocket costs will typically be lower than with a PPO.
The table below shares associated costs of the plan types, based on KFF’s 2023 Employer Health Benefits Survey. The premiums listed are for single coverage. KFF groups HMO and EPO as one plan type.
| Plan Type | Average Premium (Employer) | Average Premium (Employee) | Average General Annual Deducible |
| HMO | $6,783 | $1,420 | $1,200 |
| PPO | $7,399 | $1,507 | $1,281 |
2023 Mercer research found the average employee contribution for EPO plans was 24% lower for single coverage than with PPO. For employers, the average cost of EPO coverage was 9% lower than the cost of PPO coverage, on a per-employee basis.
The likelihood of having a general annual deductible varies by plan type, according to KFF. 33% of covered employees in HMO plans do not have a general annual deductible for single coverage, compared to 10% of workers enrolled in PPOs.
HMO vs PPO vs EPO: Which Plan is Best?
HMO plans prioritize cost-effectiveness and preventive care, while PPO plans offer more flexibility. EPO plans strike a balance between cost and flexibility. Ultimately, the best health insurance plan for your company depends on your organizational goals, challenges, workforce demographics, and budget.
To make an informed decision, consider surveying your employees about their preferred benefits. Understanding their healthcare needs and preferences can help you tailor offerings to align with their expectations.
You can also provide options for employees to choose from. This allows them to choose the plan that best fits their individual and family needs, ultimately enhancing employee satisfaction and engagement.
Managing multiple plans increases the administrative work and compliance required. To mitigate this, consider leveraging benefits administration software that streamlines the enrollment process, simplifies communication, and provides data-driven insights, allowing you to efficiently manage health plan offerings while focusing on supporting employees.
How Paycor Helps
Paycor specializes in helping businesses implement benefit plans that attract and retain top talent, while reducing the associated administrative burden. With automated workflows, detailed reporting, and an open enrollment wizard, our Benefits Administration Software empowers HR leaders to manage benefits more efficiently and effectively. Request a product tour today.
FAQS about HMO, PPO, and EPO Plans?
Want to learn more about the differences between HMO, PPO, and EPO plans? Read on!
What’s the difference between in-network and out-of-network coverage?
In-network coverage means you pay lower rates by using doctors and facilities contracted with your plan, while out-of-network care usually costs more and may have limited coverage.
Does Medicare offer HMO, PPO, and EPO options?
Yes. Medicare Advantage (Part C) includes HMO and PPO options, while EPOs are less common but may be available depending on your location and insurer.
How do referrals work under each HMO, PPO, and EPO plans?
HMO plans usually require a referral from a primary care physician to see a specialist, while PPO and EPO plans typically allow you to see specialists directly without a referral.
Do HMO or PPO plans cover dental?
Most standard HMO and PPO health plans do not include dental coverage, but many insurers offer separate dental plans that can be purchased in addition to medical insurance.